Images/noimage.png
Adim82
Polio
~1.4 mins read
Introduction
Poliomyelitis(polio) is an infectious viral disease which usually affects young children. In this review paper i will discuss how polio is transmitted, how it invades the nervous system and cause paralysis, epidemiology, clinical signs and symptoms of affected individuals, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of such patients. I will also discuss the challenges faced with the global ambition of completely irradiating polio disease despite the availability of an effective vaccine.
Poliomyelitis(polio) is an infectious viral disease which usually affects young children. In this review paper i will discuss how polio is transmitted, how it invades the nervous system and cause paralysis, epidemiology, clinical signs and symptoms of affected individuals, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of such patients. I will also discuss the challenges faced with the global ambition of completely irradiating polio disease despite the availability of an effective vaccine.
Discussion(Body)
Polio is a disabling and life threatening disease caused by the poliovirus. Polio virus is transmitted from person to person and causes paralysis by infecting a person spinal cord (WHO,2019)
Polio is a disabling and life threatening disease caused by the poliovirus. Polio virus is transmitted from person to person and causes paralysis by infecting a person spinal cord (WHO,2019)
Transmission
It is very contagious and it is transmitted through person to person contact. It lives in an infected person throat and intestines. It enters the body through the mouth and spread through contact with feces of infected people or droplets from a sneeze or cough of an infected person(CDC,2019). Infected people can spread the virus to others immediately before and up to 2 weeks after symptoms appear. People who do not have symptoms can still pass the virus to others and make them sick (CDC, 2019)
It is very contagious and it is transmitted through person to person contact. It lives in an infected person throat and intestines. It enters the body through the mouth and spread through contact with feces of infected people or droplets from a sneeze or cough of an infected person(CDC,2019). Infected people can spread the virus to others immediately before and up to 2 weeks after symptoms appear. People who do not have symptoms can still pass the virus to others and make them sick (CDC, 2019)
Signs and symptoms of polio
Most people who get infected with poliovirus will not have any visible symptoms.1 out of 4 people with poliovirus will have flu like signs that may include sore throat, fever, tiredness, nausea, headache(CDC, 2019).
The symptoms usually last 2 to 5 days then stop on their own.
A smaller proportion of people that have poliovirus infection will develop more serious symptoms including paresthesia, meningitis, and paralysis.
Paralysis is the most dangerous symptom associated with polio because it can cause permanent disability and death. Between 4 to 10 out of 100 persons who have paralysis from poliovirus die. This is because the virus affects the muscles that help with breathing.
Even kids who seem to fully recover can develop new muscle pain, weakness, or paralysis as adults, 15 or 40 years later. This is called post-polio syndrome. (CDC, 2019)
Most people who get infected with poliovirus will not have any visible symptoms.1 out of 4 people with poliovirus will have flu like signs that may include sore throat, fever, tiredness, nausea, headache(CDC, 2019).
The symptoms usually last 2 to 5 days then stop on their own.
A smaller proportion of people that have poliovirus infection will develop more serious symptoms including paresthesia, meningitis, and paralysis.
Paralysis is the most dangerous symptom associated with polio because it can cause permanent disability and death. Between 4 to 10 out of 100 persons who have paralysis from poliovirus die. This is because the virus affects the muscles that help with breathing.
Even kids who seem to fully recover can develop new muscle pain, weakness, or paralysis as adults, 15 or 40 years later. This is called post-polio syndrome. (CDC, 2019)
Images/noimage.png
Adim82
Coombs Reagent
~1.1 mins read
3. What is Coombs reagent? Describe with the aid of diagrams the diagnostic tests in which this reagent is used.
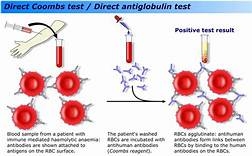
Coombs reagent (also known as Coombs antiglobulin or antihuman globulin) is used in both the direct Coombs test and the indirect Coombs test. Coombs reagent is antihuman globulin. It is made by injecting human globulin into animals, which produce polyclonal antibodies specific for human immunoglobulins and human complement system factors.More specific Coombs reagents or monoclonal antibodies can be used. Coombs test is used to detect the presence of ‘incomplete’ Rh antibodies i.e. IgG antibodies capable of sensitising RBCs but incapable of causing agglutination of RBCs (hemagglutination). Coombs test was introduced by Coombs and colleagues in 1945. The direct Coombs test, also known as direct antiglobulin test (DAT) uses antibodies directed against human proteins (primarily immunoglobulin G [IgG] and complement [C3]) to detect whether these proteins are attached to the surface of RBCs. This involves the addition of Coombs serum directly to a patient’s washed RBCs. he occurrence of agglutination means that the patient’s RBCs have been sensitized in vivo by the antibody.
Direct Coombs testing is vital for diagnosing autoimmune hemolytic anemias such as;
Coombs reagent (also known as Coombs antiglobulin or antihuman globulin) is used in both the direct Coombs test and the indirect Coombs test. Coombs reagent is antihuman globulin. It is made by injecting human globulin into animals, which produce polyclonal antibodies specific for human immunoglobulins and human complement system factors.More specific Coombs reagents or monoclonal antibodies can be used. Coombs test is used to detect the presence of ‘incomplete’ Rh antibodies i.e. IgG antibodies capable of sensitising RBCs but incapable of causing agglutination of RBCs (hemagglutination). Coombs test was introduced by Coombs and colleagues in 1945. The direct Coombs test, also known as direct antiglobulin test (DAT) uses antibodies directed against human proteins (primarily immunoglobulin G [IgG] and complement [C3]) to detect whether these proteins are attached to the surface of RBCs. This involves the addition of Coombs serum directly to a patient’s washed RBCs. he occurrence of agglutination means that the patient’s RBCs have been sensitized in vivo by the antibody.
Direct Coombs testing is vital for diagnosing autoimmune hemolytic anemias such as;
· Hemolytic transfusion reaction
· Haemolytic disease of the newborn
Autoimmune haemolytic anemia The indirect Coombs test, also known as indirect antiglobulin test (IAT) detects antibodies against human RBCs in the patient’s serum. This involves incubating a patient’s serum with RBCs of a known type and adding Coombs serum. If in vitro sensitization occurs, agglutination will result, which indicates that antibodies are present against the known blood type. Advertisement

Link socials
Matches
Loading...