Akande775
Doctor : Medical Student Of Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Nigeria
Articles
10
Followers
7
profile/942IMG_20190325_100015.jpg
Akande775

BARCELONA HAVE 332 MILLION EUROS WORTH OF TALENT ON THE MARKRT ASIDE MESSI
~1.5 mins read
According to marca:
Not everything happening at Barcelona at the moment revolves around Lionel Messi, although it may seem to be the case.
The captain's decision to leave has overshadowed, and slowed down, everything else ongoing at the Camp Nou but the club are working on rebuilding for Ronald Koeman's 2020/21 campaign.
As many as 14 players are on the market this summer, with ten of those being from the first team and the other four returning loans with no guaranteed place in the team.
They combine for 2240 games and so many of them were once untouchable players themselves.
Based on Transfermarkt's valuations, which is close to reality though not always entirely accurate due to variables, Barcelona have 332 million euros worth of talent on the market.
Sergi Roberto and Jordi Alba are the most valuable of those at 40 million euros each, followed by Samuel Umtiti (32), Sergio Busquets and Luis Suarez (28 each) and Ivan Rakitic (20).
Suarez, Arturo Vidal and Rakitic have contracts expiring in 2021 though, which means that if they are to be sold it will likely be for a slightly lower fee than what they would otherwise command.
Four of the 14 players up for sale were homegrown and didn't cost the club a cent - Carles Alena, Rafinha, Sergi Roberto and Busquets - Philippe Coutinho cost an extraordinary 120 million euros up front.
After the Brazilian come Umtiti (20 million euros), Junior Firpo (23), Vidal (19), Rakitic and Martin Braithwaite (18 each) and Jordi Alba (14), totalling 324 million euros.
The Catalans have a problem though in that not all of these players want to leave the club.
Sergi Roberto and Busquets' agents have already said that they won't leave, Jordi Alba is under contract until 2024 and Junior Firpo has just gotten in the door.
Suarez, Vidal and Rakitic's soon-expiring contracts could see them leave with relative ease, while Coutinho's situation is completely up in the air, although Messi leaving would increase his chances of staying.
Barcelona, in short, find themselves in a mess. More than half of their playing squad is up for sale, but if Messi does leave they're in a completely different situation.
profile/942IMG_20190325_100015.jpg
Akande775
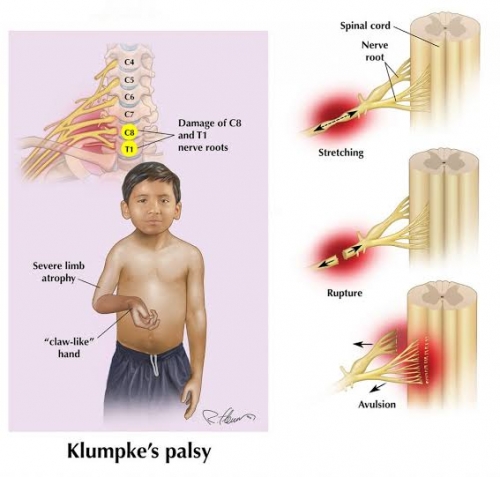
Klumpke Paralysis
~3.5 mins read
Klumpke paralysis is a neuropathy of the lower brachial plexus which may be resulted from a difficult delivery.
Usually the eighth cervical and first thoracic nerves are injured either before or after they have joined to form the lower trunk. This injury can cause a stretching (neuropraxia,), tearing (called “avulsion†when the tear is at the spine, and “rupture†when it is not), or scarring (neuroma) of the brachial plexus nerves. Most infants with Klumpke paralysis have the more mild form of injury (neuropraxia) and often recover within 6 months.
The main mechanism of injury is hyper-abduction traction and depending on the intensity, cause signs and symptoms consistent with a neurological insult.
According to the the National Institute of Neural Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), there are four types of brachial plexus injuries that cause Klumpke’s :
Avulsion, in which the nerve is severed from the spine.
Rupture, in which tearing of the nerve occurs but not at the spine.
Neuroma, in which the injured nerve has healed but can’t transmit nervous signals to the arm or hand muscles because scar tissue has formed and puts pressure on it.
Neuropraxia or stretching, in which the nerve has suffered damage but is not torn.
Causes
Risk factors for Klumpke Paralysis are:
large birth weight babies,
maternal diabetes,
multiparity,
difficult presentation,
shoulder dystocia,
forceps or vaccuum delivery,
breech position,
prolonged labor,
previous child with obstetric palsy,
intrauterine torticollis.
Less common includes tumors (neuromas, rhabdoid tumors), intrauterine compression, hemangioma and exostosis of the first rib in the child.
Signs and Symptoms
Signs and symptoms:
- “Claw hand†is a classic presentation seen where the forearm is supinated and the wrist and fingers are flexed.
Other signs and Symptoms include:
weakness and loss of movement of the arm and hand. Some babies experience drooping of the eyelid on the opposite side of the face as well. This symptom may also be referred to as Horner's syndrome.
decrease of sensation along the medial aspect of the distal upper extremity along the C8 and T1 dermatome.
myotome findings that can range from decreasing muscular strength to muscular atrophy and positional deformity.
Reflexes in the affected roots are absent.
associated injuries clavicular and humerus fractures, torticollis, cephalohematoma, and facial nerve palsy.
- An infant with a nerve injury to the lower plexus (C8-T1) holds the arm supinated, with the elbow bent and the wrist extended.
Differential Diagnosis
Erb's palsy; this injury affects the upper brachial plexus which will usually result in dermatome and myotome finds along the C5-C6 path,
Distal nerve entrapment of the ulnar nerve at either the medial epicondyle of Guyon's tunnel- produces similar neurological findings as the more proximal Klumpke's. But there is no involvement of innervation proximal to the lesion, for example, pectoralis major involvement with true ulnar nerve entrapment.
Thoracic outlet syndrome : TOS is a compression injury to the brachial plexus from a rudimentary rib, first rib, or the clavicle on the ipsilateral side, this could be post-traumatic, postural driven, and or genetic.It affects more than C8- T1 roots.
Apical lung tumor
Neurofibroma
Disc herniation
Shoulder impingement
Clavicular or vertebral fracture
Other
Management
Treatment of Klumpke’s injury in babies and children is heavily dependent on the severity and the classification of the injury.
The affected arm may be immobilized across the body for 7 to 10 days. For mild cases, gentle massage of the arm and range-of-motion exercises may be recommended.
For torn nerves (avulsion and rupture injuries), symptoms may improve with surgery.
Surgical Options:
1. Surgery on the nerves (e.g., nerve grafts and neuroma excision).
2.Tendon transfers to help the muscles that are affected by nerve damage work better.
3.Muscle transfer, in which a less important muscle or tendon is removed from another part of the body and attached to the injured arm if the muscles there deteriorate
Physiotherapy Management
Physical therapy assists in keeping the muscles and joints’ range of motion normal. Physical therapy also keeps muscles and joints to work properly and prevents stiffness in joints such as the shoulder, elbow, or wrist.
Physiotherapy majorly focuses on :
improving flexibility,
range of motion,
strength, and
dexterity
Pain control
Source: https://physio-pedia.com/Klumpke's_Paralysis?utm_source=physiopedia&utm_medium=related_articles&utm_campaign=ongoing_internal
Advertisement

Link socials
Matches
Loading...
